Business-To-Consumer (B2C) :
 Business-To-Consumer, or otherwise known as B2C explains activities of businesses serving end consumers with products and services. It is also known as a transaction that occurs between a company and a consumer. This service provides goods or services for consumers.
Business-To-Consumer, or otherwise known as B2C explains activities of businesses serving end consumers with products and services. It is also known as a transaction that occurs between a company and a consumer. This service provides goods or services for consumers.
 Consumer-To-Consumer, also known as C2C is an electronic commerce that involves the electronic-facilitated transactions between consumers through some third party. Online auction is a common example where the consumers involved posts an item for sale and other consumers bid to purchase it; the third party generally charges a flat fee or commission. The sites are only intermediaries, just there to match consumers. They do not have to check quality of the products being offered.
Consumer-To-Consumer, also known as C2C is an electronic commerce that involves the electronic-facilitated transactions between consumers through some third party. Online auction is a common example where the consumers involved posts an item for sale and other consumers bid to purchase it; the third party generally charges a flat fee or commission. The sites are only intermediaries, just there to match consumers. They do not have to check quality of the products being offered.
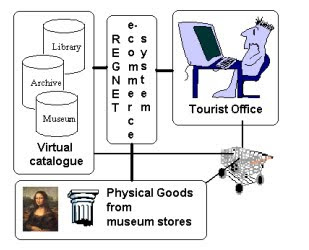
 Electronic commerce or commonly known as e-commerce consists of the buying and selling of products or services over electronic systems such as the Internet and other computer networks. The amount of trade conducted electronically has grown extraordinarily with widespread Internet usage. The use of commerce is conducted in this way, spurring and drawing on innovations in electronic funds transfer, supply chain management , Internet marketing, online transaction processing, electronic data interchange, inventory management systems, and automated data collection systems. Modern electronic commerce typically uses the World Wide Web at least at some in the transaction's life-cycle, although it can encompass a wider range of technologies such as e-mail as well.
Electronic commerce or commonly known as e-commerce consists of the buying and selling of products or services over electronic systems such as the Internet and other computer networks. The amount of trade conducted electronically has grown extraordinarily with widespread Internet usage. The use of commerce is conducted in this way, spurring and drawing on innovations in electronic funds transfer, supply chain management , Internet marketing, online transaction processing, electronic data interchange, inventory management systems, and automated data collection systems. Modern electronic commerce typically uses the World Wide Web at least at some in the transaction's life-cycle, although it can encompass a wider range of technologies such as e-mail as well.
 JavaScript is an object-orientated scripting language used to enable programmatic access to objects within both the client application and other applications. It is primarily used in the form of client-side JavaScript, implemented as an integrated component of the web browser, allowing the development of enhanced user interfaces and dynamic websites. JavaScript is a dialect of the ECMAScript standard and is characterized as a dynamic, weakly typed, prototype-based language with first class functions. JavaScript was influenced by many languages and was designed to look like Java, but to be easier for non-programmers to work with.
JavaScript is an object-orientated scripting language used to enable programmatic access to objects within both the client application and other applications. It is primarily used in the form of client-side JavaScript, implemented as an integrated component of the web browser, allowing the development of enhanced user interfaces and dynamic websites. JavaScript is a dialect of the ECMAScript standard and is characterized as a dynamic, weakly typed, prototype-based language with first class functions. JavaScript was influenced by many languages and was designed to look like Java, but to be easier for non-programmers to work with.
 Plug-ins have appeared as early as the mid 1970s, when the EDT text editor running on the Unisys VS/9 operating system using the Univac 90/60 series mainframe computer provided the ability to run a program from the editor and to allow such program to access the editor buffer, thus allowing an external program to access an edit session in memory. Plug-in consists of a computer program that interacts with a host application (e.g. web browser or an e-mail client) to provide a specific function, "on demand". Plug-in is often considered the general term compromising add-ons, extensions and themes as subcategories.
Plug-ins have appeared as early as the mid 1970s, when the EDT text editor running on the Unisys VS/9 operating system using the Univac 90/60 series mainframe computer provided the ability to run a program from the editor and to allow such program to access the editor buffer, thus allowing an external program to access an edit session in memory. Plug-in consists of a computer program that interacts with a host application (e.g. web browser or an e-mail client) to provide a specific function, "on demand". Plug-in is often considered the general term compromising add-ons, extensions and themes as subcategories.

 Business-To-Consumer, or otherwise known as B2C explains activities of businesses serving end consumers with products and services. It is also known as a transaction that occurs between a company and a consumer. This service provides goods or services for consumers.
Business-To-Consumer, or otherwise known as B2C explains activities of businesses serving end consumers with products and services. It is also known as a transaction that occurs between a company and a consumer. This service provides goods or services for consumers. Consumer-To-Consumer (C2C) :
 Consumer-To-Consumer, also known as C2C is an electronic commerce that involves the electronic-facilitated transactions between consumers through some third party. Online auction is a common example where the consumers involved posts an item for sale and other consumers bid to purchase it; the third party generally charges a flat fee or commission. The sites are only intermediaries, just there to match consumers. They do not have to check quality of the products being offered.
Consumer-To-Consumer, also known as C2C is an electronic commerce that involves the electronic-facilitated transactions between consumers through some third party. Online auction is a common example where the consumers involved posts an item for sale and other consumers bid to purchase it; the third party generally charges a flat fee or commission. The sites are only intermediaries, just there to match consumers. They do not have to check quality of the products being offered.E-Commerce :
Internet Security Suite :
When a computer connects a network and begins to communicate with each other, it is actually taking a risk. Internet security involves the protection of a computer's internet account and files from intrusion of an unknown user. Basic security measures involve protection by well selected passwords, change of file permissions and back up of computer's data. Security concerns are in some ways peripheral to normal business working, but serve to highlight just how important it is that business users feel confident when using IT systems. Whenever decisions need to be made about how to enhance a system, security will need to be held uppermost among its requirements.JavaScript :
 JavaScript is an object-orientated scripting language used to enable programmatic access to objects within both the client application and other applications. It is primarily used in the form of client-side JavaScript, implemented as an integrated component of the web browser, allowing the development of enhanced user interfaces and dynamic websites. JavaScript is a dialect of the ECMAScript standard and is characterized as a dynamic, weakly typed, prototype-based language with first class functions. JavaScript was influenced by many languages and was designed to look like Java, but to be easier for non-programmers to work with.
JavaScript is an object-orientated scripting language used to enable programmatic access to objects within both the client application and other applications. It is primarily used in the form of client-side JavaScript, implemented as an integrated component of the web browser, allowing the development of enhanced user interfaces and dynamic websites. JavaScript is a dialect of the ECMAScript standard and is characterized as a dynamic, weakly typed, prototype-based language with first class functions. JavaScript was influenced by many languages and was designed to look like Java, but to be easier for non-programmers to work with.Plug-In :
 Plug-ins have appeared as early as the mid 1970s, when the EDT text editor running on the Unisys VS/9 operating system using the Univac 90/60 series mainframe computer provided the ability to run a program from the editor and to allow such program to access the editor buffer, thus allowing an external program to access an edit session in memory. Plug-in consists of a computer program that interacts with a host application (e.g. web browser or an e-mail client) to provide a specific function, "on demand". Plug-in is often considered the general term compromising add-ons, extensions and themes as subcategories.
Plug-ins have appeared as early as the mid 1970s, when the EDT text editor running on the Unisys VS/9 operating system using the Univac 90/60 series mainframe computer provided the ability to run a program from the editor and to allow such program to access the editor buffer, thus allowing an external program to access an edit session in memory. Plug-in consists of a computer program that interacts with a host application (e.g. web browser or an e-mail client) to provide a specific function, "on demand". Plug-in is often considered the general term compromising add-ons, extensions and themes as subcategories.Spam :

The original term for 'Spam' was actually net abuse. It is also meant by the abuse of electronic messaging systems to send unsolicited bulk message s indiscriminately. While the most widely recognized form of spam is e-mail spam, the term is applied to similar abuses in other media. Spamming remains economically viable because advertisers have no operating costs beyond the management of their mailing list, and it is difficult to hold senders accountable for their mass mailings. The volume of unsolicited mail has become very high, and the spammers become numerous because the barrier to entry is so low. Spamming is universally reviled, and has been the subject of legislation in many jurisdictions.









