Sockets:
 Sockets are often made up of plastic, a metal lever or latch and metal contacts for each of the pins or land on the CPU. They are an electrical component that attaches to a printed circuit board (PCB) and is designed to house a microprocessor. It is a special type of integrated circuit socket specially designed for very high pin counts. Sockets provide many functions and one of them is to provide a physical structure to support the CPU.These things can most often be found in desktop and and server computers, particularly those that are based on the Intel x86 architecture on the motherboard.
Sockets are often made up of plastic, a metal lever or latch and metal contacts for each of the pins or land on the CPU. They are an electrical component that attaches to a printed circuit board (PCB) and is designed to house a microprocessor. It is a special type of integrated circuit socket specially designed for very high pin counts. Sockets provide many functions and one of them is to provide a physical structure to support the CPU.These things can most often be found in desktop and and server computers, particularly those that are based on the Intel x86 architecture on the motherboard.Chips:
 Also known as integrated circuit. The idea of coming up with the integrated chip was conceived by a radar scientist working for the Royal Radar Establishment of the British Ministry of Defense, Geoffrey W.A. Dummer. This is a miniaturized electronic circuit which mainly consist of semiconductor devices as well as passive components that has been manufactured in the surface of a thin subtrate of semiconductor material. The switch of tiny transistors into a small chips was an enormous improvement over the manual assembly of circuits. Almost all electronics components that are in use today have these chips implanted in them and have revolutionized the world of electronics.
Also known as integrated circuit. The idea of coming up with the integrated chip was conceived by a radar scientist working for the Royal Radar Establishment of the British Ministry of Defense, Geoffrey W.A. Dummer. This is a miniaturized electronic circuit which mainly consist of semiconductor devices as well as passive components that has been manufactured in the surface of a thin subtrate of semiconductor material. The switch of tiny transistors into a small chips was an enormous improvement over the manual assembly of circuits. Almost all electronics components that are in use today have these chips implanted in them and have revolutionized the world of electronics.Slots:
 A slot is meant by the opening in the computer where you can insert a printed circuit board. It is located inside a computer (back of the computer) on the motherboard or riser board that allows additional boards to be connected to it. They also provide access to the AGP, PCIe, PCI, and ISA on the motherboard. A person would need an expension card to actually use the expansion slot opening. The expansion slots also allow the computer system to communicate with the outside world.
A slot is meant by the opening in the computer where you can insert a printed circuit board. It is located inside a computer (back of the computer) on the motherboard or riser board that allows additional boards to be connected to it. They also provide access to the AGP, PCIe, PCI, and ISA on the motherboard. A person would need an expension card to actually use the expansion slot opening. The expansion slots also allow the computer system to communicate with the outside world.Bus Lines:
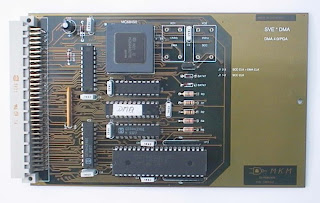 During the early days, computer bus lines were literally parallel electrical buses with multiple connections. However, this term is now used for any physical arrangements that provides the same logical functionally as a parallel electrical bus. Nowadays. the modern computer buses can use both parallel and bit-serial connections, and can be wired in either a multidrop or daisy chain topology. The advantage of using computer buses is that any computer can be accessed directly and messages can be sent in a relatively simple and fast way. But there is also a disadvantage that is a scheduler is required to organize the traffic by assigning frequencies and priorities to each channel.
During the early days, computer bus lines were literally parallel electrical buses with multiple connections. However, this term is now used for any physical arrangements that provides the same logical functionally as a parallel electrical bus. Nowadays. the modern computer buses can use both parallel and bit-serial connections, and can be wired in either a multidrop or daisy chain topology. The advantage of using computer buses is that any computer can be accessed directly and messages can be sent in a relatively simple and fast way. But there is also a disadvantage that is a scheduler is required to organize the traffic by assigning frequencies and priorities to each channel.Graphics Card:
 Graphics card can also be called as video cards, video adapter, graphics-accelerator card or display adapter. It is an expansion card whose function is to generate and output images to display. Many of these graphic cards offer added functions, while other modern high performance cards are used for more graphically demanding purposes such as computer games. The hardware of the graphic card can be integrated on the motherboard, often occurring with early machines. The first graphic card was released with the first IBM PC, and was developed in 1981.
Graphics card can also be called as video cards, video adapter, graphics-accelerator card or display adapter. It is an expansion card whose function is to generate and output images to display. Many of these graphic cards offer added functions, while other modern high performance cards are used for more graphically demanding purposes such as computer games. The hardware of the graphic card can be integrated on the motherboard, often occurring with early machines. The first graphic card was released with the first IBM PC, and was developed in 1981.Sound Card:
 Also known as the audio card. This is a computer expansion card that facilitates the input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under control of other programs. The few typical uses of sound cards include providing the audio component for multimedia applications like video editing to entertainment. Many of the computers manufactured today have sound capabilities built in, while others require additional expansion cards to provide for audio capability. Furthermore, sound cards usually feature a digital-to-analog converter (DAC), which converts recorded or generated digital data into an analog format.
Also known as the audio card. This is a computer expansion card that facilitates the input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under control of other programs. The few typical uses of sound cards include providing the audio component for multimedia applications like video editing to entertainment. Many of the computers manufactured today have sound capabilities built in, while others require additional expansion cards to provide for audio capability. Furthermore, sound cards usually feature a digital-to-analog converter (DAC), which converts recorded or generated digital data into an analog format.Modem Card:
 A modem card allows users to connect to the internet using a network. A modem card can either be wireless or installed inside a user's PC. Wireless modem card allows Internet access by communicating with a router that is already connected to a user's PC. Furthermore, the modem card that is placed in the PCI slot usually operates at a much faster speed compared to a wireless one. This modem card is usually recommended for an average user but can cost more than other modem cards.The modem cared that connects to motherboard of the PC is cheaper compared to a PCI card, however, it is not as reliable.
A modem card allows users to connect to the internet using a network. A modem card can either be wireless or installed inside a user's PC. Wireless modem card allows Internet access by communicating with a router that is already connected to a user's PC. Furthermore, the modem card that is placed in the PCI slot usually operates at a much faster speed compared to a wireless one. This modem card is usually recommended for an average user but can cost more than other modem cards.The modem cared that connects to motherboard of the PC is cheaper compared to a PCI card, however, it is not as reliable.Network Interface Card:
 Is a network interface devise (NID) in the form of circuit card that is installed an an expansion slot of a computer to provide network access. This is the card that physically makes the connection between the computer and the network cable. These cards come in ISA and PCI versions and they are made by companies like 3Com and LinkSys. Today, Ethernet is the local area network standard, whereas in the past, Token Ring and Apple's LocalTalk networks were widely used. The adapters of network interface cards are wired to a network hub, switch or router, using twisted wire pair cables.
Is a network interface devise (NID) in the form of circuit card that is installed an an expansion slot of a computer to provide network access. This is the card that physically makes the connection between the computer and the network cable. These cards come in ISA and PCI versions and they are made by companies like 3Com and LinkSys. Today, Ethernet is the local area network standard, whereas in the past, Token Ring and Apple's LocalTalk networks were widely used. The adapters of network interface cards are wired to a network hub, switch or router, using twisted wire pair cables.Plug and Play:
 Plug and Play (PnP) defines the ability to add a new component to a system and have it work automatically without having to do any technical analysis or manual configuration. It is a standard from Intel for peripheral expansion on a PC. This term is a catchy phrase used to describe devices that work with a computer system as soon as that are connected. The user does not have to manually install drivers for the device or even tell the computer that a new device has been added . Instead, the computer will automatically recognize the device, loads new drivers for the hardware if needed, and begins to work with the newly connected device. Plug and Play can also be used to describe internal hardware.
Plug and Play (PnP) defines the ability to add a new component to a system and have it work automatically without having to do any technical analysis or manual configuration. It is a standard from Intel for peripheral expansion on a PC. This term is a catchy phrase used to describe devices that work with a computer system as soon as that are connected. The user does not have to manually install drivers for the device or even tell the computer that a new device has been added . Instead, the computer will automatically recognize the device, loads new drivers for the hardware if needed, and begins to work with the newly connected device. Plug and Play can also be used to describe internal hardware.Serial Port:
 The serial port is a type of connection on PCs that is used for peripheral such as mice, gaming controllers, modems, and older printers. Also, it is sometimes called a COM port or an RS-232 port, which is a technical name. A serial port only transmit one bit of data at a time, whereas a parallel port can transmit many bits at once. Therefore, a serial port is possibly the slowest port that you'll find on a PC. Most newer computers have already replaced with much faster and more compatible USB ports. While such interfaces as Ethernet, FireWare, and USB all send data as a serial stream, this term "serial port" usually identifies hardware more or less complaint to the RS-232 standard, intended to interface with a modem or with a similar communication device.
The serial port is a type of connection on PCs that is used for peripheral such as mice, gaming controllers, modems, and older printers. Also, it is sometimes called a COM port or an RS-232 port, which is a technical name. A serial port only transmit one bit of data at a time, whereas a parallel port can transmit many bits at once. Therefore, a serial port is possibly the slowest port that you'll find on a PC. Most newer computers have already replaced with much faster and more compatible USB ports. While such interfaces as Ethernet, FireWare, and USB all send data as a serial stream, this term "serial port" usually identifies hardware more or less complaint to the RS-232 standard, intended to interface with a modem or with a similar communication device.Parallel Port:
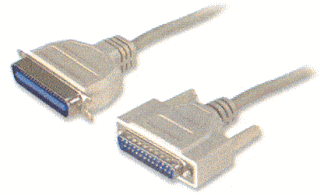 This interface is found on the back of older PCs and is used for connecting external devices such as printers or scanners. It uses a 25-pin connector (DB-25) and is quite big if you compared it to other new interfaces. It is sometimes called a Centronics interface since Centronics was the company that designed the original parallel port standard. It is also sometimes referred to as a printer port because the printer is the device most commonly attached to the parallel port. Now, there is a new parallel port that is called the Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP).
This interface is found on the back of older PCs and is used for connecting external devices such as printers or scanners. It uses a 25-pin connector (DB-25) and is quite big if you compared it to other new interfaces. It is sometimes called a Centronics interface since Centronics was the company that designed the original parallel port standard. It is also sometimes referred to as a printer port because the printer is the device most commonly attached to the parallel port. Now, there is a new parallel port that is called the Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP).Universal Serial Bus Port:
Better known as the US
 B port. It is said to be a standard cable connection interface on personal computers and consumer electronics. USB ports allow stand-alone electronics devices to be connected via cables to a computer. In current times, this device has successfully worked its way into the hearts of many computer peripherals makers such as printers,external storage, mp3 players, and camera makers. It has become a standard use USB as a medium connecting these peripherals to a computer. A computer usually ships in with 6 to 8 of these ports. If more is needed, you can extend it with a USB hub. There are two types of USB standard that exist, which is the wired and the wireless USB standard but only the wired version involves USB ports and cables.
B port. It is said to be a standard cable connection interface on personal computers and consumer electronics. USB ports allow stand-alone electronics devices to be connected via cables to a computer. In current times, this device has successfully worked its way into the hearts of many computer peripherals makers such as printers,external storage, mp3 players, and camera makers. It has become a standard use USB as a medium connecting these peripherals to a computer. A computer usually ships in with 6 to 8 of these ports. If more is needed, you can extend it with a USB hub. There are two types of USB standard that exist, which is the wired and the wireless USB standard but only the wired version involves USB ports and cables.Firewire Port:
 Firewire is a high-speed interface that has become a hot new standard for connecting peripherals. Firewire was created by Apple Computer in the mid-1990's, and can be used to connect devices like digital cameras, mp3 players such as the Apple iPod, hard drives, and audio interfaces to your computer. A standard Firewire connection can transfer data at 400 Mbps, which is roughly 30 times faster than USB 1.1. This extremely fast speed allows for quick transfer of large video files which is great for video-editing professionals.
Firewire is a high-speed interface that has become a hot new standard for connecting peripherals. Firewire was created by Apple Computer in the mid-1990's, and can be used to connect devices like digital cameras, mp3 players such as the Apple iPod, hard drives, and audio interfaces to your computer. A standard Firewire connection can transfer data at 400 Mbps, which is roughly 30 times faster than USB 1.1. This extremely fast speed allows for quick transfer of large video files which is great for video-editing professionals.