Node: A node is said to be devices that are connected to a computer network. Examples of nodes are: printers, PDAs, computers, cell phones, or various other network appliances. On an IP network, a node is any device with an IP address. This term also refers to a small technological object that has a particular function, but is often thought of as a novelty. They are invariably considered to be more unusually or more cleverly designed than normal technological objects at the time of their invention.
A node is said to be devices that are connected to a computer network. Examples of nodes are: printers, PDAs, computers, cell phones, or various other network appliances. On an IP network, a node is any device with an IP address. This term also refers to a small technological object that has a particular function, but is often thought of as a novelty. They are invariably considered to be more unusually or more cleverly designed than normal technological objects at the time of their invention.
Client: A client can also be called as a purchaser, buyer or customer. This term is usually referred to a current or potential buyer or user of products of an individual or organization, which is called the vendor , supplier or seller. However, in certain contexts, the term client also includes by extension anyone who uses or experiences the service of another. They can also be the viewers of product or service that is being sold despite deciding to not buy them. Nowadays, companies sent out clients to deal with the other company that they will be collaborating with and they will close a deal with these clients instead of having big office meetings.
A client can also be called as a purchaser, buyer or customer. This term is usually referred to a current or potential buyer or user of products of an individual or organization, which is called the vendor , supplier or seller. However, in certain contexts, the term client also includes by extension anyone who uses or experiences the service of another. They can also be the viewers of product or service that is being sold despite deciding to not buy them. Nowadays, companies sent out clients to deal with the other company that they will be collaborating with and they will close a deal with these clients instead of having big office meetings.
Server: A server is basically a node that shares resources with other nodes. It is sometimes referred to as an enterprise server. It is a computer system that provides essential services across a network, to private users inside a large organizations or to public users on the Internet. Many of the dedicated servers are specialized in performing specific tasks. For example, database server, application server, communication server, file server, printer server, web server, and many others. The enterprise server is known to be very fault tolerant, for even a short-term failure can cost more than purchasing and installing the system.
A server is basically a node that shares resources with other nodes. It is sometimes referred to as an enterprise server. It is a computer system that provides essential services across a network, to private users inside a large organizations or to public users on the Internet. Many of the dedicated servers are specialized in performing specific tasks. For example, database server, application server, communication server, file server, printer server, web server, and many others. The enterprise server is known to be very fault tolerant, for even a short-term failure can cost more than purchasing and installing the system.
Hub: This is the central nodes for other nodes. They are sometimes built into equipment, such as keyboards, monitors, printers, and computers. Physically separated hubs come in a wide variety of form factors: from boxes connectible with a long cable, to small designs that can be directly plugged into a USB port.
This is the central nodes for other nodes. They are sometimes built into equipment, such as keyboards, monitors, printers, and computers. Physically separated hubs come in a wide variety of form factors: from boxes connectible with a long cable, to small designs that can be directly plugged into a USB port.
Network Interface Card (NIC): Is a network interface devise (NID) in the form of circuit card that is installed an an expansion slot of a computer to provide network access. This is the card that physically makes the connection between the computer and the network cable. These cards come in ISA and PCI versions and they are made by companies like 3Com and LinkSys. Today, Ethernet is the local area network standard, whereas in the past, Token Ring and Apple's LocalTalk networks were widely used. The adapters of network interface cards are wired to a network hub, switch or router, using twisted wire pair cables.
Is a network interface devise (NID) in the form of circuit card that is installed an an expansion slot of a computer to provide network access. This is the card that physically makes the connection between the computer and the network cable. These cards come in ISA and PCI versions and they are made by companies like 3Com and LinkSys. Today, Ethernet is the local area network standard, whereas in the past, Token Ring and Apple's LocalTalk networks were widely used. The adapters of network interface cards are wired to a network hub, switch or router, using twisted wire pair cables.
Network Operating System (NOS):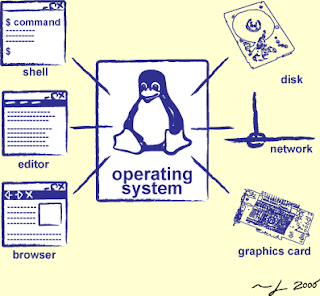 A network operating system is a system that control and coordinate the activities of all computers and other devices in the network. It is also a system that contains components and programs that allow a computer on a network to serve requests from other computers for data and provide access to other resources such as printers and file systems.
A network operating system is a system that control and coordinate the activities of all computers and other devices in the network. It is also a system that contains components and programs that allow a computer on a network to serve requests from other computers for data and provide access to other resources such as printers and file systems.
Host Computer: It is meant by the main or controlling computer connected to other computers or terminals to which it provides data or computing services via a network. It is a large centralized computer, and is usually a minicomputer or a mainframe. A host computer is similar to a server in a client-server architecture. In the modern peer to peer networking (such as networking over the Internet) every computer is a peer and also a host to every other computer connected to the network. This term reflects the biological relationship between a host and parasites.
It is meant by the main or controlling computer connected to other computers or terminals to which it provides data or computing services via a network. It is a large centralized computer, and is usually a minicomputer or a mainframe. A host computer is similar to a server in a client-server architecture. In the modern peer to peer networking (such as networking over the Internet) every computer is a peer and also a host to every other computer connected to the network. This term reflects the biological relationship between a host and parasites.
Network Manager: A network manager is basically a computer specialist responsible for efficient network operations and implementation of new networks. They are the ones that are responsible for the operation and administration of their company's internal networks, servers, e-mails, and network security systems. Part of their duty is also administration and maintenance of mission critical web and database servers hosted mainly within the company's own data centre in London, some hosted externally. Their job is to also Configure and set-up of all new server systems required either internally for the company’s activities or for external clients. Also, administration of email servers (predominantly MS Exchange) for company-wide email and for management of email handling systems for clients across many domains. Maintenance of existing Anti-Spam and anti-virus systems and the setting of new Anti-Spam policies.
A network manager is basically a computer specialist responsible for efficient network operations and implementation of new networks. They are the ones that are responsible for the operation and administration of their company's internal networks, servers, e-mails, and network security systems. Part of their duty is also administration and maintenance of mission critical web and database servers hosted mainly within the company's own data centre in London, some hosted externally. Their job is to also Configure and set-up of all new server systems required either internally for the company’s activities or for external clients. Also, administration of email servers (predominantly MS Exchange) for company-wide email and for management of email handling systems for clients across many domains. Maintenance of existing Anti-Spam and anti-virus systems and the setting of new Anti-Spam policies.
Saturday, March 6, 2010
Communication & Networks
Posted by Eunice Chuang at 6:52 AM 0 comments
Monday, February 8, 2010
System Unit
Sockets:
 Sockets are often made up of plastic, a metal lever or latch and metal contacts for each of the pins or land on the CPU. They are an electrical component that attaches to a printed circuit board (PCB) and is designed to house a microprocessor. It is a special type of integrated circuit socket specially designed for very high pin counts. Sockets provide many functions and one of them is to provide a physical structure to support the CPU.These things can most often be found in desktop and and server computers, particularly those that are based on the Intel x86 architecture on the motherboard.
Sockets are often made up of plastic, a metal lever or latch and metal contacts for each of the pins or land on the CPU. They are an electrical component that attaches to a printed circuit board (PCB) and is designed to house a microprocessor. It is a special type of integrated circuit socket specially designed for very high pin counts. Sockets provide many functions and one of them is to provide a physical structure to support the CPU.These things can most often be found in desktop and and server computers, particularly those that are based on the Intel x86 architecture on the motherboard.Chips:
 Also known as integrated circuit. The idea of coming up with the integrated chip was conceived by a radar scientist working for the Royal Radar Establishment of the British Ministry of Defense, Geoffrey W.A. Dummer. This is a miniaturized electronic circuit which mainly consist of semiconductor devices as well as passive components that has been manufactured in the surface of a thin subtrate of semiconductor material. The switch of tiny transistors into a small chips was an enormous improvement over the manual assembly of circuits. Almost all electronics components that are in use today have these chips implanted in them and have revolutionized the world of electronics.
Also known as integrated circuit. The idea of coming up with the integrated chip was conceived by a radar scientist working for the Royal Radar Establishment of the British Ministry of Defense, Geoffrey W.A. Dummer. This is a miniaturized electronic circuit which mainly consist of semiconductor devices as well as passive components that has been manufactured in the surface of a thin subtrate of semiconductor material. The switch of tiny transistors into a small chips was an enormous improvement over the manual assembly of circuits. Almost all electronics components that are in use today have these chips implanted in them and have revolutionized the world of electronics.Slots:
 A slot is meant by the opening in the computer where you can insert a printed circuit board. It is located inside a computer (back of the computer) on the motherboard or riser board that allows additional boards to be connected to it. They also provide access to the AGP, PCIe, PCI, and ISA on the motherboard. A person would need an expension card to actually use the expansion slot opening. The expansion slots also allow the computer system to communicate with the outside world.
A slot is meant by the opening in the computer where you can insert a printed circuit board. It is located inside a computer (back of the computer) on the motherboard or riser board that allows additional boards to be connected to it. They also provide access to the AGP, PCIe, PCI, and ISA on the motherboard. A person would need an expension card to actually use the expansion slot opening. The expansion slots also allow the computer system to communicate with the outside world.Bus Lines:
 During the early days, computer bus lines were literally parallel electrical buses with multiple connections. However, this term is now used for any physical arrangements that provides the same logical functionally as a parallel electrical bus. Nowadays. the modern computer buses can use both parallel and bit-serial connections, and can be wired in either a multidrop or daisy chain topology. The advantage of using computer buses is that any computer can be accessed directly and messages can be sent in a relatively simple and fast way. But there is also a disadvantage that is a scheduler is required to organize the traffic by assigning frequencies and priorities to each channel.
During the early days, computer bus lines were literally parallel electrical buses with multiple connections. However, this term is now used for any physical arrangements that provides the same logical functionally as a parallel electrical bus. Nowadays. the modern computer buses can use both parallel and bit-serial connections, and can be wired in either a multidrop or daisy chain topology. The advantage of using computer buses is that any computer can be accessed directly and messages can be sent in a relatively simple and fast way. But there is also a disadvantage that is a scheduler is required to organize the traffic by assigning frequencies and priorities to each channel.Graphics Card:
 Graphics card can also be called as video cards, video adapter, graphics-accelerator card or display adapter. It is an expansion card whose function is to generate and output images to display. Many of these graphic cards offer added functions, while other modern high performance cards are used for more graphically demanding purposes such as computer games. The hardware of the graphic card can be integrated on the motherboard, often occurring with early machines. The first graphic card was released with the first IBM PC, and was developed in 1981.
Graphics card can also be called as video cards, video adapter, graphics-accelerator card or display adapter. It is an expansion card whose function is to generate and output images to display. Many of these graphic cards offer added functions, while other modern high performance cards are used for more graphically demanding purposes such as computer games. The hardware of the graphic card can be integrated on the motherboard, often occurring with early machines. The first graphic card was released with the first IBM PC, and was developed in 1981.Sound Card:
 Also known as the audio card. This is a computer expansion card that facilitates the input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under control of other programs. The few typical uses of sound cards include providing the audio component for multimedia applications like video editing to entertainment. Many of the computers manufactured today have sound capabilities built in, while others require additional expansion cards to provide for audio capability. Furthermore, sound cards usually feature a digital-to-analog converter (DAC), which converts recorded or generated digital data into an analog format.
Also known as the audio card. This is a computer expansion card that facilitates the input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under control of other programs. The few typical uses of sound cards include providing the audio component for multimedia applications like video editing to entertainment. Many of the computers manufactured today have sound capabilities built in, while others require additional expansion cards to provide for audio capability. Furthermore, sound cards usually feature a digital-to-analog converter (DAC), which converts recorded or generated digital data into an analog format.Modem Card:
 A modem card allows users to connect to the internet using a network. A modem card can either be wireless or installed inside a user's PC. Wireless modem card allows Internet access by communicating with a router that is already connected to a user's PC. Furthermore, the modem card that is placed in the PCI slot usually operates at a much faster speed compared to a wireless one. This modem card is usually recommended for an average user but can cost more than other modem cards.The modem cared that connects to motherboard of the PC is cheaper compared to a PCI card, however, it is not as reliable.
A modem card allows users to connect to the internet using a network. A modem card can either be wireless or installed inside a user's PC. Wireless modem card allows Internet access by communicating with a router that is already connected to a user's PC. Furthermore, the modem card that is placed in the PCI slot usually operates at a much faster speed compared to a wireless one. This modem card is usually recommended for an average user but can cost more than other modem cards.The modem cared that connects to motherboard of the PC is cheaper compared to a PCI card, however, it is not as reliable.Network Interface Card:
 Is a network interface devise (NID) in the form of circuit card that is installed an an expansion slot of a computer to provide network access. This is the card that physically makes the connection between the computer and the network cable. These cards come in ISA and PCI versions and they are made by companies like 3Com and LinkSys. Today, Ethernet is the local area network standard, whereas in the past, Token Ring and Apple's LocalTalk networks were widely used. The adapters of network interface cards are wired to a network hub, switch or router, using twisted wire pair cables.
Is a network interface devise (NID) in the form of circuit card that is installed an an expansion slot of a computer to provide network access. This is the card that physically makes the connection between the computer and the network cable. These cards come in ISA and PCI versions and they are made by companies like 3Com and LinkSys. Today, Ethernet is the local area network standard, whereas in the past, Token Ring and Apple's LocalTalk networks were widely used. The adapters of network interface cards are wired to a network hub, switch or router, using twisted wire pair cables.Plug and Play:
 Plug and Play (PnP) defines the ability to add a new component to a system and have it work automatically without having to do any technical analysis or manual configuration. It is a standard from Intel for peripheral expansion on a PC. This term is a catchy phrase used to describe devices that work with a computer system as soon as that are connected. The user does not have to manually install drivers for the device or even tell the computer that a new device has been added . Instead, the computer will automatically recognize the device, loads new drivers for the hardware if needed, and begins to work with the newly connected device. Plug and Play can also be used to describe internal hardware.
Plug and Play (PnP) defines the ability to add a new component to a system and have it work automatically without having to do any technical analysis or manual configuration. It is a standard from Intel for peripheral expansion on a PC. This term is a catchy phrase used to describe devices that work with a computer system as soon as that are connected. The user does not have to manually install drivers for the device or even tell the computer that a new device has been added . Instead, the computer will automatically recognize the device, loads new drivers for the hardware if needed, and begins to work with the newly connected device. Plug and Play can also be used to describe internal hardware.Serial Port:
 The serial port is a type of connection on PCs that is used for peripheral such as mice, gaming controllers, modems, and older printers. Also, it is sometimes called a COM port or an RS-232 port, which is a technical name. A serial port only transmit one bit of data at a time, whereas a parallel port can transmit many bits at once. Therefore, a serial port is possibly the slowest port that you'll find on a PC. Most newer computers have already replaced with much faster and more compatible USB ports. While such interfaces as Ethernet, FireWare, and USB all send data as a serial stream, this term "serial port" usually identifies hardware more or less complaint to the RS-232 standard, intended to interface with a modem or with a similar communication device.
The serial port is a type of connection on PCs that is used for peripheral such as mice, gaming controllers, modems, and older printers. Also, it is sometimes called a COM port or an RS-232 port, which is a technical name. A serial port only transmit one bit of data at a time, whereas a parallel port can transmit many bits at once. Therefore, a serial port is possibly the slowest port that you'll find on a PC. Most newer computers have already replaced with much faster and more compatible USB ports. While such interfaces as Ethernet, FireWare, and USB all send data as a serial stream, this term "serial port" usually identifies hardware more or less complaint to the RS-232 standard, intended to interface with a modem or with a similar communication device.Parallel Port:
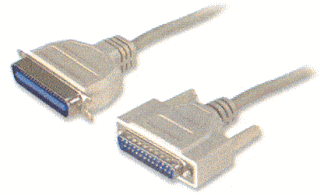 This interface is found on the back of older PCs and is used for connecting external devices such as printers or scanners. It uses a 25-pin connector (DB-25) and is quite big if you compared it to other new interfaces. It is sometimes called a Centronics interface since Centronics was the company that designed the original parallel port standard. It is also sometimes referred to as a printer port because the printer is the device most commonly attached to the parallel port. Now, there is a new parallel port that is called the Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP).
This interface is found on the back of older PCs and is used for connecting external devices such as printers or scanners. It uses a 25-pin connector (DB-25) and is quite big if you compared it to other new interfaces. It is sometimes called a Centronics interface since Centronics was the company that designed the original parallel port standard. It is also sometimes referred to as a printer port because the printer is the device most commonly attached to the parallel port. Now, there is a new parallel port that is called the Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP).Universal Serial Bus Port:
Better known as the US
 B port. It is said to be a standard cable connection interface on personal computers and consumer electronics. USB ports allow stand-alone electronics devices to be connected via cables to a computer. In current times, this device has successfully worked its way into the hearts of many computer peripherals makers such as printers,external storage, mp3 players, and camera makers. It has become a standard use USB as a medium connecting these peripherals to a computer. A computer usually ships in with 6 to 8 of these ports. If more is needed, you can extend it with a USB hub. There are two types of USB standard that exist, which is the wired and the wireless USB standard but only the wired version involves USB ports and cables.
B port. It is said to be a standard cable connection interface on personal computers and consumer electronics. USB ports allow stand-alone electronics devices to be connected via cables to a computer. In current times, this device has successfully worked its way into the hearts of many computer peripherals makers such as printers,external storage, mp3 players, and camera makers. It has become a standard use USB as a medium connecting these peripherals to a computer. A computer usually ships in with 6 to 8 of these ports. If more is needed, you can extend it with a USB hub. There are two types of USB standard that exist, which is the wired and the wireless USB standard but only the wired version involves USB ports and cables.Firewire Port:
 Firewire is a high-speed interface that has become a hot new standard for connecting peripherals. Firewire was created by Apple Computer in the mid-1990's, and can be used to connect devices like digital cameras, mp3 players such as the Apple iPod, hard drives, and audio interfaces to your computer. A standard Firewire connection can transfer data at 400 Mbps, which is roughly 30 times faster than USB 1.1. This extremely fast speed allows for quick transfer of large video files which is great for video-editing professionals.
Firewire is a high-speed interface that has become a hot new standard for connecting peripherals. Firewire was created by Apple Computer in the mid-1990's, and can be used to connect devices like digital cameras, mp3 players such as the Apple iPod, hard drives, and audio interfaces to your computer. A standard Firewire connection can transfer data at 400 Mbps, which is roughly 30 times faster than USB 1.1. This extremely fast speed allows for quick transfer of large video files which is great for video-editing professionals.Posted by Eunice Chuang at 8:26 PM 0 comments
Monday, January 25, 2010
The Internet, The Web & E-Commerce
Business-To-Consumer (B2C) :
 Business-To-Consumer, or otherwise known as B2C explains activities of businesses serving end consumers with products and services. It is also known as a transaction that occurs between a company and a consumer. This service provides goods or services for consumers.
Business-To-Consumer, or otherwise known as B2C explains activities of businesses serving end consumers with products and services. It is also known as a transaction that occurs between a company and a consumer. This service provides goods or services for consumers.
 Consumer-To-Consumer, also known as C2C is an electronic commerce that involves the electronic-facilitated transactions between consumers through some third party. Online auction is a common example where the consumers involved posts an item for sale and other consumers bid to purchase it; the third party generally charges a flat fee or commission. The sites are only intermediaries, just there to match consumers. They do not have to check quality of the products being offered.
Consumer-To-Consumer, also known as C2C is an electronic commerce that involves the electronic-facilitated transactions between consumers through some third party. Online auction is a common example where the consumers involved posts an item for sale and other consumers bid to purchase it; the third party generally charges a flat fee or commission. The sites are only intermediaries, just there to match consumers. They do not have to check quality of the products being offered.
 Electronic commerce or commonly known as e-commerce consists of the buying and selling of products or services over electronic systems such as the Internet and other computer networks. The amount of trade conducted electronically has grown extraordinarily with widespread Internet usage. The use of commerce is conducted in this way, spurring and drawing on innovations in electronic funds transfer, supply chain management , Internet marketing, online transaction processing, electronic data interchange, inventory management systems, and automated data collection systems. Modern electronic commerce typically uses the World Wide Web at least at some in the transaction's life-cycle, although it can encompass a wider range of technologies such as e-mail as well.
Electronic commerce or commonly known as e-commerce consists of the buying and selling of products or services over electronic systems such as the Internet and other computer networks. The amount of trade conducted electronically has grown extraordinarily with widespread Internet usage. The use of commerce is conducted in this way, spurring and drawing on innovations in electronic funds transfer, supply chain management , Internet marketing, online transaction processing, electronic data interchange, inventory management systems, and automated data collection systems. Modern electronic commerce typically uses the World Wide Web at least at some in the transaction's life-cycle, although it can encompass a wider range of technologies such as e-mail as well.
 JavaScript is an object-orientated scripting language used to enable programmatic access to objects within both the client application and other applications. It is primarily used in the form of client-side JavaScript, implemented as an integrated component of the web browser, allowing the development of enhanced user interfaces and dynamic websites. JavaScript is a dialect of the ECMAScript standard and is characterized as a dynamic, weakly typed, prototype-based language with first class functions. JavaScript was influenced by many languages and was designed to look like Java, but to be easier for non-programmers to work with.
JavaScript is an object-orientated scripting language used to enable programmatic access to objects within both the client application and other applications. It is primarily used in the form of client-side JavaScript, implemented as an integrated component of the web browser, allowing the development of enhanced user interfaces and dynamic websites. JavaScript is a dialect of the ECMAScript standard and is characterized as a dynamic, weakly typed, prototype-based language with first class functions. JavaScript was influenced by many languages and was designed to look like Java, but to be easier for non-programmers to work with.
 Plug-ins have appeared as early as the mid 1970s, when the EDT text editor running on the Unisys VS/9 operating system using the Univac 90/60 series mainframe computer provided the ability to run a program from the editor and to allow such program to access the editor buffer, thus allowing an external program to access an edit session in memory. Plug-in consists of a computer program that interacts with a host application (e.g. web browser or an e-mail client) to provide a specific function, "on demand". Plug-in is often considered the general term compromising add-ons, extensions and themes as subcategories.
Plug-ins have appeared as early as the mid 1970s, when the EDT text editor running on the Unisys VS/9 operating system using the Univac 90/60 series mainframe computer provided the ability to run a program from the editor and to allow such program to access the editor buffer, thus allowing an external program to access an edit session in memory. Plug-in consists of a computer program that interacts with a host application (e.g. web browser or an e-mail client) to provide a specific function, "on demand". Plug-in is often considered the general term compromising add-ons, extensions and themes as subcategories.

 Business-To-Consumer, or otherwise known as B2C explains activities of businesses serving end consumers with products and services. It is also known as a transaction that occurs between a company and a consumer. This service provides goods or services for consumers.
Business-To-Consumer, or otherwise known as B2C explains activities of businesses serving end consumers with products and services. It is also known as a transaction that occurs between a company and a consumer. This service provides goods or services for consumers. Consumer-To-Consumer (C2C) :
 Consumer-To-Consumer, also known as C2C is an electronic commerce that involves the electronic-facilitated transactions between consumers through some third party. Online auction is a common example where the consumers involved posts an item for sale and other consumers bid to purchase it; the third party generally charges a flat fee or commission. The sites are only intermediaries, just there to match consumers. They do not have to check quality of the products being offered.
Consumer-To-Consumer, also known as C2C is an electronic commerce that involves the electronic-facilitated transactions between consumers through some third party. Online auction is a common example where the consumers involved posts an item for sale and other consumers bid to purchase it; the third party generally charges a flat fee or commission. The sites are only intermediaries, just there to match consumers. They do not have to check quality of the products being offered.E-Commerce :
Internet Security Suite :
When a computer connects a network and begins to communicate with each other, it is actually taking a risk. Internet security involves the protection of a computer's internet account and files from intrusion of an unknown user. Basic security measures involve protection by well selected passwords, change of file permissions and back up of computer's data. Security concerns are in some ways peripheral to normal business working, but serve to highlight just how important it is that business users feel confident when using IT systems. Whenever decisions need to be made about how to enhance a system, security will need to be held uppermost among its requirements.JavaScript :
 JavaScript is an object-orientated scripting language used to enable programmatic access to objects within both the client application and other applications. It is primarily used in the form of client-side JavaScript, implemented as an integrated component of the web browser, allowing the development of enhanced user interfaces and dynamic websites. JavaScript is a dialect of the ECMAScript standard and is characterized as a dynamic, weakly typed, prototype-based language with first class functions. JavaScript was influenced by many languages and was designed to look like Java, but to be easier for non-programmers to work with.
JavaScript is an object-orientated scripting language used to enable programmatic access to objects within both the client application and other applications. It is primarily used in the form of client-side JavaScript, implemented as an integrated component of the web browser, allowing the development of enhanced user interfaces and dynamic websites. JavaScript is a dialect of the ECMAScript standard and is characterized as a dynamic, weakly typed, prototype-based language with first class functions. JavaScript was influenced by many languages and was designed to look like Java, but to be easier for non-programmers to work with.Plug-In :
 Plug-ins have appeared as early as the mid 1970s, when the EDT text editor running on the Unisys VS/9 operating system using the Univac 90/60 series mainframe computer provided the ability to run a program from the editor and to allow such program to access the editor buffer, thus allowing an external program to access an edit session in memory. Plug-in consists of a computer program that interacts with a host application (e.g. web browser or an e-mail client) to provide a specific function, "on demand". Plug-in is often considered the general term compromising add-ons, extensions and themes as subcategories.
Plug-ins have appeared as early as the mid 1970s, when the EDT text editor running on the Unisys VS/9 operating system using the Univac 90/60 series mainframe computer provided the ability to run a program from the editor and to allow such program to access the editor buffer, thus allowing an external program to access an edit session in memory. Plug-in consists of a computer program that interacts with a host application (e.g. web browser or an e-mail client) to provide a specific function, "on demand". Plug-in is often considered the general term compromising add-ons, extensions and themes as subcategories.Spam :

The original term for 'Spam' was actually net abuse. It is also meant by the abuse of electronic messaging systems to send unsolicited bulk message s indiscriminately. While the most widely recognized form of spam is e-mail spam, the term is applied to similar abuses in other media. Spamming remains economically viable because advertisers have no operating costs beyond the management of their mailing list, and it is difficult to hold senders accountable for their mass mailings. The volume of unsolicited mail has become very high, and the spammers become numerous because the barrier to entry is so low. Spamming is universally reviled, and has been the subject of legislation in many jurisdictions.
Posted by Eunice Chuang at 9:26 PM 0 comments
Monday, January 18, 2010
Careers In IT
Webmaster:
 Webmasters can also be known as web architects, web developers, site authors, website administrators, or webmiester. Basically, a webmaster's job is to maintain Web sites for companies and individuals on the World Wide Web. He or she is also responsible to ensure that the web that he or she is in charge are operating accurately. Although a webmaster sometimes assumes the role of a web designer, the main job of a webmaster is to monitor, improve, and update the performance of existing Web sites. Therefore, a webmaster must know about the client's business and which industry it belongs to. Depending on the websites they manage, webmasters typically know scripting languages such as PHP, Perl and Javascript. A webmaster's job also ranges from constructing a website to management of the content, advertising, marketing and order fulfillment for the website.
Webmasters can also be known as web architects, web developers, site authors, website administrators, or webmiester. Basically, a webmaster's job is to maintain Web sites for companies and individuals on the World Wide Web. He or she is also responsible to ensure that the web that he or she is in charge are operating accurately. Although a webmaster sometimes assumes the role of a web designer, the main job of a webmaster is to monitor, improve, and update the performance of existing Web sites. Therefore, a webmaster must know about the client's business and which industry it belongs to. Depending on the websites they manage, webmasters typically know scripting languages such as PHP, Perl and Javascript. A webmaster's job also ranges from constructing a website to management of the content, advertising, marketing and order fulfillment for the website.
Computer Support Specialist:
 For those who are experiencing provblems with their computer, you can always consult a computer support specialist. A computer supprt specialist's job is to basically to help people who don't have technical expertise. Those who go to them for help will have to describe the problems and commands that led them up to the problem stated. Then, the specialist will duplicate the problem to his or her computer to help them in solving the problem. When the problem is discovered, the specialist will explain how the problem is caused and the steps to be taken to help fix it. Other computer support specialists known as technical support specialists provide support to people in the information processing department of a company. Personnals at an office can also go to the specialist for help in using the computer system and to answer questions about getting started with the system.
For those who are experiencing provblems with their computer, you can always consult a computer support specialist. A computer supprt specialist's job is to basically to help people who don't have technical expertise. Those who go to them for help will have to describe the problems and commands that led them up to the problem stated. Then, the specialist will duplicate the problem to his or her computer to help them in solving the problem. When the problem is discovered, the specialist will explain how the problem is caused and the steps to be taken to help fix it. Other computer support specialists known as technical support specialists provide support to people in the information processing department of a company. Personnals at an office can also go to the specialist for help in using the computer system and to answer questions about getting started with the system.
Technical Writer:
 A technical writers job is basically to explain scientific and technical ideas that are difficult for the average readers to read. Also, many technical writers who are in this specialty are former scientists and technicians. So who does technical writers work for? Well, they can be found working for book, magazine, or newspapers publishers. These people can also be found working in other industries. Thousands of business and trade magazines and papers are published by industries and publishing firms to keep readers informed about special fields. Therefore, industrial publications companies often hire technical writers to write and edit their publications. One of the reasons technical writers are employed in these industries is to prepare articles for other firms.
A technical writers job is basically to explain scientific and technical ideas that are difficult for the average readers to read. Also, many technical writers who are in this specialty are former scientists and technicians. So who does technical writers work for? Well, they can be found working for book, magazine, or newspapers publishers. These people can also be found working in other industries. Thousands of business and trade magazines and papers are published by industries and publishing firms to keep readers informed about special fields. Therefore, industrial publications companies often hire technical writers to write and edit their publications. One of the reasons technical writers are employed in these industries is to prepare articles for other firms.
Software Engineer:

Database Administrator:
 Database administrators use database software to manage
Database administrators use database software to manage
and store information. Their job is also to make sure that the data they store is backed up regularly, stored efficiently, and that the data is secured from any unauthorized access. A database administrator has to also always ensure the data is available by maximizing database uptime. Other tasks of a database administrator is to develop and design database strategies, monitoring, and improving database performance and capacity, and planning for future expansion requirements. They may also plan, co-ordinate and implement security measures to safeguard the database.
System Analyst:
 First of all, a system analyst's job is responsible for planning, coordinating, researching, and recommending software and system choices to meet an organization's business requirements. System analyst may work on improving computer systems that are already in use. Those who are facing problems can consult a system analyst. A typical problem for a system analyst would be to develop a software for a new computerized inventory system used by a large retail store. Sometimes, a system analyst also modify systems when changes are made in the task the computer has to complete.
First of all, a system analyst's job is responsible for planning, coordinating, researching, and recommending software and system choices to meet an organization's business requirements. System analyst may work on improving computer systems that are already in use. Those who are facing problems can consult a system analyst. A typical problem for a system analyst would be to develop a software for a new computerized inventory system used by a large retail store. Sometimes, a system analyst also modify systems when changes are made in the task the computer has to complete.
Programmer:
 Basically, a computer programmer's job is to write step-by-step instructions that direct computers to process information. The kind of work or projects that a computer programmer does consists of very large range. The work that a programmer does also depends on their employers. Programmers work in manufacturing, industry, engineering, government offices, hospitals and educational institutions. Usually programmers receive very detailed job descriptions that identify the goal of the program. After receiving them, they will prepare system flow charts that show diagrammatically how information will flow through the computer and its peripheral or related equipment. When all the set up is complete, the programmers will then write the actual program using special computer languages. They will also have to test the program to see whether it is running properly as expected. When everything is perfectly fine, the program is able to be used.
Basically, a computer programmer's job is to write step-by-step instructions that direct computers to process information. The kind of work or projects that a computer programmer does consists of very large range. The work that a programmer does also depends on their employers. Programmers work in manufacturing, industry, engineering, government offices, hospitals and educational institutions. Usually programmers receive very detailed job descriptions that identify the goal of the program. After receiving them, they will prepare system flow charts that show diagrammatically how information will flow through the computer and its peripheral or related equipment. When all the set up is complete, the programmers will then write the actual program using special computer languages. They will also have to test the program to see whether it is running properly as expected. When everything is perfectly fine, the program is able to be used.
 Webmasters can also be known as web architects, web developers, site authors, website administrators, or webmiester. Basically, a webmaster's job is to maintain Web sites for companies and individuals on the World Wide Web. He or she is also responsible to ensure that the web that he or she is in charge are operating accurately. Although a webmaster sometimes assumes the role of a web designer, the main job of a webmaster is to monitor, improve, and update the performance of existing Web sites. Therefore, a webmaster must know about the client's business and which industry it belongs to. Depending on the websites they manage, webmasters typically know scripting languages such as PHP, Perl and Javascript. A webmaster's job also ranges from constructing a website to management of the content, advertising, marketing and order fulfillment for the website.
Webmasters can also be known as web architects, web developers, site authors, website administrators, or webmiester. Basically, a webmaster's job is to maintain Web sites for companies and individuals on the World Wide Web. He or she is also responsible to ensure that the web that he or she is in charge are operating accurately. Although a webmaster sometimes assumes the role of a web designer, the main job of a webmaster is to monitor, improve, and update the performance of existing Web sites. Therefore, a webmaster must know about the client's business and which industry it belongs to. Depending on the websites they manage, webmasters typically know scripting languages such as PHP, Perl and Javascript. A webmaster's job also ranges from constructing a website to management of the content, advertising, marketing and order fulfillment for the website.Computer Support Specialist:
 For those who are experiencing provblems with their computer, you can always consult a computer support specialist. A computer supprt specialist's job is to basically to help people who don't have technical expertise. Those who go to them for help will have to describe the problems and commands that led them up to the problem stated. Then, the specialist will duplicate the problem to his or her computer to help them in solving the problem. When the problem is discovered, the specialist will explain how the problem is caused and the steps to be taken to help fix it. Other computer support specialists known as technical support specialists provide support to people in the information processing department of a company. Personnals at an office can also go to the specialist for help in using the computer system and to answer questions about getting started with the system.
For those who are experiencing provblems with their computer, you can always consult a computer support specialist. A computer supprt specialist's job is to basically to help people who don't have technical expertise. Those who go to them for help will have to describe the problems and commands that led them up to the problem stated. Then, the specialist will duplicate the problem to his or her computer to help them in solving the problem. When the problem is discovered, the specialist will explain how the problem is caused and the steps to be taken to help fix it. Other computer support specialists known as technical support specialists provide support to people in the information processing department of a company. Personnals at an office can also go to the specialist for help in using the computer system and to answer questions about getting started with the system.Technical Writer:
 A technical writers job is basically to explain scientific and technical ideas that are difficult for the average readers to read. Also, many technical writers who are in this specialty are former scientists and technicians. So who does technical writers work for? Well, they can be found working for book, magazine, or newspapers publishers. These people can also be found working in other industries. Thousands of business and trade magazines and papers are published by industries and publishing firms to keep readers informed about special fields. Therefore, industrial publications companies often hire technical writers to write and edit their publications. One of the reasons technical writers are employed in these industries is to prepare articles for other firms.
A technical writers job is basically to explain scientific and technical ideas that are difficult for the average readers to read. Also, many technical writers who are in this specialty are former scientists and technicians. So who does technical writers work for? Well, they can be found working for book, magazine, or newspapers publishers. These people can also be found working in other industries. Thousands of business and trade magazines and papers are published by industries and publishing firms to keep readers informed about special fields. Therefore, industrial publications companies often hire technical writers to write and edit their publications. One of the reasons technical writers are employed in these industries is to prepare articles for other firms.
Software engineering is one of the most popular occupations in IT in terms of the number of software engineers employed. Software engineers are sometimes referred to as computer programmers or software developers. A software engineer researches, designs and develops software systems to meet with software requirements. Being in this profession requires knowledge of a variety of computer programming languages and applications. This is all due to the wide variety of work that they can be involved in. Work activities of a software engineer includes researching, designing and writing new software programs. Sometimes, their job also requires them to develop existing programs by analysing and identifying areas for modification.
Network Administrator:
 Basically, a network administrators job is to oversee computer networks to make sure that they function smoothly. A network can be as small as two or three computers or as large as an Internet. The job of an network administrator is to set up the infrastructure of a computer network. Also, they usually configure and manage an existing network. He or she may be responsible for customizing the network to an individuals company's need by connecting the necessary hardware and software to the network. Other than that, they are also required to monitor the performance of the network and troubleshoots problems such as slow performance or network crashes. Network administrators must also work with individual users who are having network problems that are not experienced by other users. Some network problems may result in the loss or corruption of data stored on the server. Therefore, the administrator must develop, install, and maintain emergency systems to back up the main network server.
Basically, a network administrators job is to oversee computer networks to make sure that they function smoothly. A network can be as small as two or three computers or as large as an Internet. The job of an network administrator is to set up the infrastructure of a computer network. Also, they usually configure and manage an existing network. He or she may be responsible for customizing the network to an individuals company's need by connecting the necessary hardware and software to the network. Other than that, they are also required to monitor the performance of the network and troubleshoots problems such as slow performance or network crashes. Network administrators must also work with individual users who are having network problems that are not experienced by other users. Some network problems may result in the loss or corruption of data stored on the server. Therefore, the administrator must develop, install, and maintain emergency systems to back up the main network server.
 Basically, a network administrators job is to oversee computer networks to make sure that they function smoothly. A network can be as small as two or three computers or as large as an Internet. The job of an network administrator is to set up the infrastructure of a computer network. Also, they usually configure and manage an existing network. He or she may be responsible for customizing the network to an individuals company's need by connecting the necessary hardware and software to the network. Other than that, they are also required to monitor the performance of the network and troubleshoots problems such as slow performance or network crashes. Network administrators must also work with individual users who are having network problems that are not experienced by other users. Some network problems may result in the loss or corruption of data stored on the server. Therefore, the administrator must develop, install, and maintain emergency systems to back up the main network server.
Basically, a network administrators job is to oversee computer networks to make sure that they function smoothly. A network can be as small as two or three computers or as large as an Internet. The job of an network administrator is to set up the infrastructure of a computer network. Also, they usually configure and manage an existing network. He or she may be responsible for customizing the network to an individuals company's need by connecting the necessary hardware and software to the network. Other than that, they are also required to monitor the performance of the network and troubleshoots problems such as slow performance or network crashes. Network administrators must also work with individual users who are having network problems that are not experienced by other users. Some network problems may result in the loss or corruption of data stored on the server. Therefore, the administrator must develop, install, and maintain emergency systems to back up the main network server.Database Administrator:
 Database administrators use database software to manage
Database administrators use database software to manageand store information. Their job is also to make sure that the data they store is backed up regularly, stored efficiently, and that the data is secured from any unauthorized access. A database administrator has to also always ensure the data is available by maximizing database uptime. Other tasks of a database administrator is to develop and design database strategies, monitoring, and improving database performance and capacity, and planning for future expansion requirements. They may also plan, co-ordinate and implement security measures to safeguard the database.
System Analyst:
 First of all, a system analyst's job is responsible for planning, coordinating, researching, and recommending software and system choices to meet an organization's business requirements. System analyst may work on improving computer systems that are already in use. Those who are facing problems can consult a system analyst. A typical problem for a system analyst would be to develop a software for a new computerized inventory system used by a large retail store. Sometimes, a system analyst also modify systems when changes are made in the task the computer has to complete.
First of all, a system analyst's job is responsible for planning, coordinating, researching, and recommending software and system choices to meet an organization's business requirements. System analyst may work on improving computer systems that are already in use. Those who are facing problems can consult a system analyst. A typical problem for a system analyst would be to develop a software for a new computerized inventory system used by a large retail store. Sometimes, a system analyst also modify systems when changes are made in the task the computer has to complete.Programmer:
 Basically, a computer programmer's job is to write step-by-step instructions that direct computers to process information. The kind of work or projects that a computer programmer does consists of very large range. The work that a programmer does also depends on their employers. Programmers work in manufacturing, industry, engineering, government offices, hospitals and educational institutions. Usually programmers receive very detailed job descriptions that identify the goal of the program. After receiving them, they will prepare system flow charts that show diagrammatically how information will flow through the computer and its peripheral or related equipment. When all the set up is complete, the programmers will then write the actual program using special computer languages. They will also have to test the program to see whether it is running properly as expected. When everything is perfectly fine, the program is able to be used.
Basically, a computer programmer's job is to write step-by-step instructions that direct computers to process information. The kind of work or projects that a computer programmer does consists of very large range. The work that a programmer does also depends on their employers. Programmers work in manufacturing, industry, engineering, government offices, hospitals and educational institutions. Usually programmers receive very detailed job descriptions that identify the goal of the program. After receiving them, they will prepare system flow charts that show diagrammatically how information will flow through the computer and its peripheral or related equipment. When all the set up is complete, the programmers will then write the actual program using special computer languages. They will also have to test the program to see whether it is running properly as expected. When everything is perfectly fine, the program is able to be used. Posted by Eunice Chuang at 9:37 PM 0 comments
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

