Node: A node is said to be devices that are connected to a computer network. Examples of nodes are: printers, PDAs, computers, cell phones, or various other network appliances. On an IP network, a node is any device with an IP address. This term also refers to a small technological object that has a particular function, but is often thought of as a novelty. They are invariably considered to be more unusually or more cleverly designed than normal technological objects at the time of their invention.
A node is said to be devices that are connected to a computer network. Examples of nodes are: printers, PDAs, computers, cell phones, or various other network appliances. On an IP network, a node is any device with an IP address. This term also refers to a small technological object that has a particular function, but is often thought of as a novelty. They are invariably considered to be more unusually or more cleverly designed than normal technological objects at the time of their invention.
Client: A client can also be called as a purchaser, buyer or customer. This term is usually referred to a current or potential buyer or user of products of an individual or organization, which is called the vendor , supplier or seller. However, in certain contexts, the term client also includes by extension anyone who uses or experiences the service of another. They can also be the viewers of product or service that is being sold despite deciding to not buy them. Nowadays, companies sent out clients to deal with the other company that they will be collaborating with and they will close a deal with these clients instead of having big office meetings.
A client can also be called as a purchaser, buyer or customer. This term is usually referred to a current or potential buyer or user of products of an individual or organization, which is called the vendor , supplier or seller. However, in certain contexts, the term client also includes by extension anyone who uses or experiences the service of another. They can also be the viewers of product or service that is being sold despite deciding to not buy them. Nowadays, companies sent out clients to deal with the other company that they will be collaborating with and they will close a deal with these clients instead of having big office meetings.
Server: A server is basically a node that shares resources with other nodes. It is sometimes referred to as an enterprise server. It is a computer system that provides essential services across a network, to private users inside a large organizations or to public users on the Internet. Many of the dedicated servers are specialized in performing specific tasks. For example, database server, application server, communication server, file server, printer server, web server, and many others. The enterprise server is known to be very fault tolerant, for even a short-term failure can cost more than purchasing and installing the system.
A server is basically a node that shares resources with other nodes. It is sometimes referred to as an enterprise server. It is a computer system that provides essential services across a network, to private users inside a large organizations or to public users on the Internet. Many of the dedicated servers are specialized in performing specific tasks. For example, database server, application server, communication server, file server, printer server, web server, and many others. The enterprise server is known to be very fault tolerant, for even a short-term failure can cost more than purchasing and installing the system.
Hub: This is the central nodes for other nodes. They are sometimes built into equipment, such as keyboards, monitors, printers, and computers. Physically separated hubs come in a wide variety of form factors: from boxes connectible with a long cable, to small designs that can be directly plugged into a USB port.
This is the central nodes for other nodes. They are sometimes built into equipment, such as keyboards, monitors, printers, and computers. Physically separated hubs come in a wide variety of form factors: from boxes connectible with a long cable, to small designs that can be directly plugged into a USB port.
Network Interface Card (NIC): Is a network interface devise (NID) in the form of circuit card that is installed an an expansion slot of a computer to provide network access. This is the card that physically makes the connection between the computer and the network cable. These cards come in ISA and PCI versions and they are made by companies like 3Com and LinkSys. Today, Ethernet is the local area network standard, whereas in the past, Token Ring and Apple's LocalTalk networks were widely used. The adapters of network interface cards are wired to a network hub, switch or router, using twisted wire pair cables.
Is a network interface devise (NID) in the form of circuit card that is installed an an expansion slot of a computer to provide network access. This is the card that physically makes the connection between the computer and the network cable. These cards come in ISA and PCI versions and they are made by companies like 3Com and LinkSys. Today, Ethernet is the local area network standard, whereas in the past, Token Ring and Apple's LocalTalk networks were widely used. The adapters of network interface cards are wired to a network hub, switch or router, using twisted wire pair cables.
Network Operating System (NOS):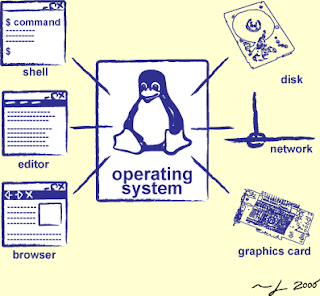 A network operating system is a system that control and coordinate the activities of all computers and other devices in the network. It is also a system that contains components and programs that allow a computer on a network to serve requests from other computers for data and provide access to other resources such as printers and file systems.
A network operating system is a system that control and coordinate the activities of all computers and other devices in the network. It is also a system that contains components and programs that allow a computer on a network to serve requests from other computers for data and provide access to other resources such as printers and file systems.
Host Computer: It is meant by the main or controlling computer connected to other computers or terminals to which it provides data or computing services via a network. It is a large centralized computer, and is usually a minicomputer or a mainframe. A host computer is similar to a server in a client-server architecture. In the modern peer to peer networking (such as networking over the Internet) every computer is a peer and also a host to every other computer connected to the network. This term reflects the biological relationship between a host and parasites.
It is meant by the main or controlling computer connected to other computers or terminals to which it provides data or computing services via a network. It is a large centralized computer, and is usually a minicomputer or a mainframe. A host computer is similar to a server in a client-server architecture. In the modern peer to peer networking (such as networking over the Internet) every computer is a peer and also a host to every other computer connected to the network. This term reflects the biological relationship between a host and parasites.
Network Manager: A network manager is basically a computer specialist responsible for efficient network operations and implementation of new networks. They are the ones that are responsible for the operation and administration of their company's internal networks, servers, e-mails, and network security systems. Part of their duty is also administration and maintenance of mission critical web and database servers hosted mainly within the company's own data centre in London, some hosted externally. Their job is to also Configure and set-up of all new server systems required either internally for the company’s activities or for external clients. Also, administration of email servers (predominantly MS Exchange) for company-wide email and for management of email handling systems for clients across many domains. Maintenance of existing Anti-Spam and anti-virus systems and the setting of new Anti-Spam policies.
A network manager is basically a computer specialist responsible for efficient network operations and implementation of new networks. They are the ones that are responsible for the operation and administration of their company's internal networks, servers, e-mails, and network security systems. Part of their duty is also administration and maintenance of mission critical web and database servers hosted mainly within the company's own data centre in London, some hosted externally. Their job is to also Configure and set-up of all new server systems required either internally for the company’s activities or for external clients. Also, administration of email servers (predominantly MS Exchange) for company-wide email and for management of email handling systems for clients across many domains. Maintenance of existing Anti-Spam and anti-virus systems and the setting of new Anti-Spam policies.
Saturday, March 6, 2010
Communication & Networks
Posted by Eunice Chuang at 6:52 AM
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)

0 comments:
Post a Comment